Advanced Perspective Sketching Techniques Elevate Industrial Design Practice
Industrial designers boost depth and realism by mastering proportion guidelines, multi‑point perspectives, and cylinder rendering.
Sketca
Fundamental Guidelines for Consistent Proportions
Industrial designers rely on precise proportion rules to ensure that every element of a product sketch aligns with real‑world dimensions. The source material emphasizes the use of guidelines to maintain consistent proportions across a drawing, a practice that prevents distortion when transitioning from concept to detailed rendering. By establishing a baseline grid, designers can measure and replicate sizes accurately, fostering visual harmony throughout the sketch. This foundational step is critical before introducing complex perspective systems, as it anchors the composition and supports subsequent depth cues. (Copy from MCHIP)
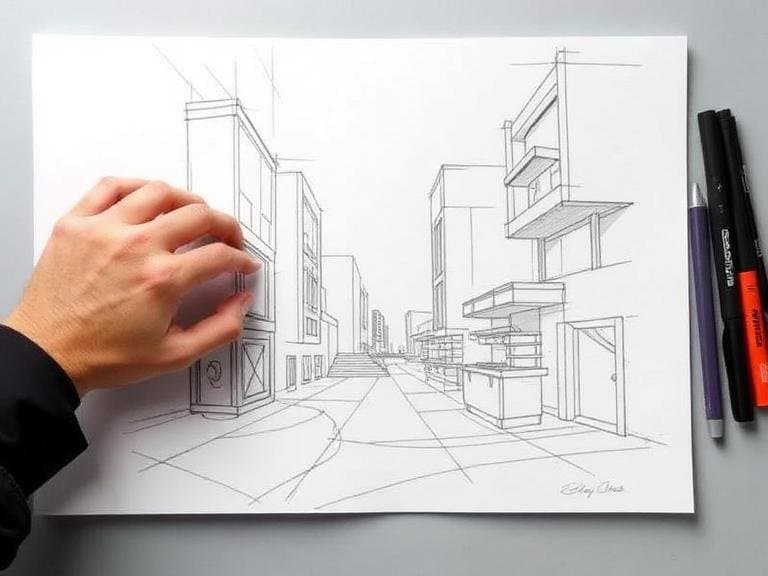
Mastering One‑, Two‑, and Three‑Point Perspectives
Perspective drawing creates the illusion of three‑dimensional space on a flat surface, a technique essential for industrial designers seeking to communicate form and function. The instructional material outlines a progressive approach: start with one‑point perspective to depict objects directly facing the viewer, then advance to two‑point perspective for angled views, and finally adopt three‑point perspective for dramatic, high‑or‑low angle compositions. Each method adds a vanishing point that guides lines toward a common horizon, reinforcing depth perception. Practicing these perspectives systematically enables designers to render products from any angle, enhancing both visual impact and technical clarity. (Copy from MCHIP)
Rendering Cylindrical Forms in Three‑Dimensional Space
Cylinders are a recurring geometric element in product design, appearing in components such as handles, shafts, and containers. A dedicated guide on drawing cylinders recommends turning the paper to align the drawing surface with the cylinder’s axis, a technique that accelerates the sketching process and improves accuracy. By rotating the sheet, the artist can apply consistent ellipses for the cylinder’s ends and maintain uniform curvature along its length. Practical exercises focus on visualizing the cylinder’s orientation within a perspective grid, ensuring that the rendered form integrates seamlessly with surrounding elements. This method cultivates speed and confidence when depicting rounded components in complex assemblies. (Copy from TIP 406)
Integrating Freehand Techniques and Interior Sketching
Beyond structured perspective, freehand sketching empowers industrial designers to convey ideas rapidly and with expressive nuance. An industrial design course led by Hector Silva emphasizes a curriculum that progresses from foundational drawing to advanced freehand techniques, allowing designers to capture organic shapes and material textures without relying solely on strict guidelines. Complementary insights from an interior sketching blog highlight the application of hand‑rendered perspective in architectural contexts, reinforcing the transferability of these skills to product environments. By blending freehand fluidity with disciplined perspective, designers achieve sketches that are both technically accurate and visually engaging. (Copy from Offsite) (Copy from Olga's blog)
Practical Exercises for Skill Development
To translate theory into proficiency, designers are encouraged to engage in targeted exercises. One set involves sketching a series of objects—such as a coffee mug, a lamp, and a handheld device—using one‑, two‑, and three‑point perspectives consecutively. Another exercise focuses on drawing cylinders from varying angles, applying the paper‑turning method to reinforce spatial understanding. Additionally, designers should allocate time for freehand sessions, sketching interior spaces or product setups without grids to cultivate gestural confidence. Repeating these drills cultivates muscle memory, accelerates decision‑making, and refines the ability to visualize complex forms swiftly. (Copy from Sketching: Drawing Techniques for Product Designers)
Application in Product Design Workflow
Incorporating advanced perspective sketching into the product design workflow yields tangible benefits. Early‑stage concept sketches enriched with accurate perspective provide stakeholders with a clearer sense of scale and ergonomics. Detailed renderings that correctly depict cylinders and other geometric features reduce ambiguity during engineering hand‑off, minimizing revisions. Moreover, the combination of structured perspective and freehand expression supports iterative design, enabling rapid exploration of alternative forms while preserving visual fidelity. This integrated approach aligns with industry expectations for clear, compelling visual communication throughout the development cycle. (Copy from Sketching Drawing Techniques For Product Designer)
Technology and Tools Supporting Perspective Sketching
While traditional pen‑and‑paper methods remain foundational, digital tools augment perspective accuracy. Software that offers perspective grids and customizable vanishing points assists designers in maintaining consistent depth cues across multiple sketches. Tablet interfaces with tilt sensitivity replicate the paper‑turning technique for cylinders, allowing artists to adjust stroke angles dynamically. Nevertheless, the core principles outlined in the source materials—guideline usage, point perspective mastery, and freehand integration—remain applicable regardless of medium, underscoring their enduring relevance. (Copy from Perspective drawing tips)
Continuous Learning and Community Resources
Staying current with perspective techniques requires engagement with educational resources and professional communities. Workshops, such as the one featuring Hector Silva, provide hands‑on instruction and peer feedback. Online blogs dedicated to interior sketching and perspective drawing share case studies and step‑by‑step tutorials that reinforce classroom learning. By regularly reviewing updated guides—like the 2025 and 2026 publications referenced—designers ensure that their skill set evolves alongside emerging design trends and technological advancements. (Copy from Interior sketching — #1 Blog on Interior Design Drawing)
Conclusion: Elevating Design Through Mastery of Perspective
Advanced perspective sketching stands as a cornerstone of effective industrial design communication. Mastery of proportion guidelines, multi‑point perspective systems, cylinder rendering techniques, and freehand expression equips designers to produce sketches that are both technically precise and creatively compelling. The synthesis of these methods, supported by structured practice and continuous learning, empowers designers to articulate complex three‑dimensional concepts with confidence and clarity, ultimately enhancing the product development process from ideation to final presentation. (Copy from Sketching: Drawing Techniques for Product Designers)